C-Reactive Protein CRP Test
C-reactive protein CRP is a protein made in the liver that indicates the amount of inflammation in the body. Like elevated homocysteine, a high CRP level increases one’s vulnerability to cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer’s, and cancer. Such an increase in CRP levels may be caused by infection, inflammation, trauma, diabetes, as well as certain medicines. In the absence of these main factors, elevated CRP indicates future risks of heart attack.
This article was last reviewed on 10 April 2019. This article was last modified on 14 February 2020.
In addition, increased systemic inflammation is a sign of aging. Therefore, C-reactive protein (CRP) can be classified as a marker of healthy aging1.
It has been found that this marker predicts well the risk of developing age-related diseases and human life span2.
What is the difference between CRP and hs-CRP?
As you’ve no doubt guessed, the difference between CRP and hs-CRP is contained in the “hs” abbreviation – “high sensitivity.”
RELATED ARTICLES
Traditionally, CRP, or C-reactive protein, is measured down to concentrations of 3 to 5 mg/L; hs-CRP is measured down to concentrations of approximately 0.3 mg/L. This improved sensitivity allows hs-CRP to be used to detect low levels of chronic inflammation.
So, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) lab test is a marker of inflammation that predicts incident myocardial infarction, stroke, peripheral arterial disease, and sudden cardiac death among healthy individuals with no history of cardiovascular disease. Elderly people with high CRP levels are more vulnerable to serious diseases than their relatives with low C-reactive protein levels.
Which level is considered the norm?
Concentrations less than 1 mg/L indicate low risk of cardiovascular disease.
1 to 2,9 mg/L levels suggest average risk. Concentrations above 3.0 mg/L indicate a high risk of cardiovascular disease
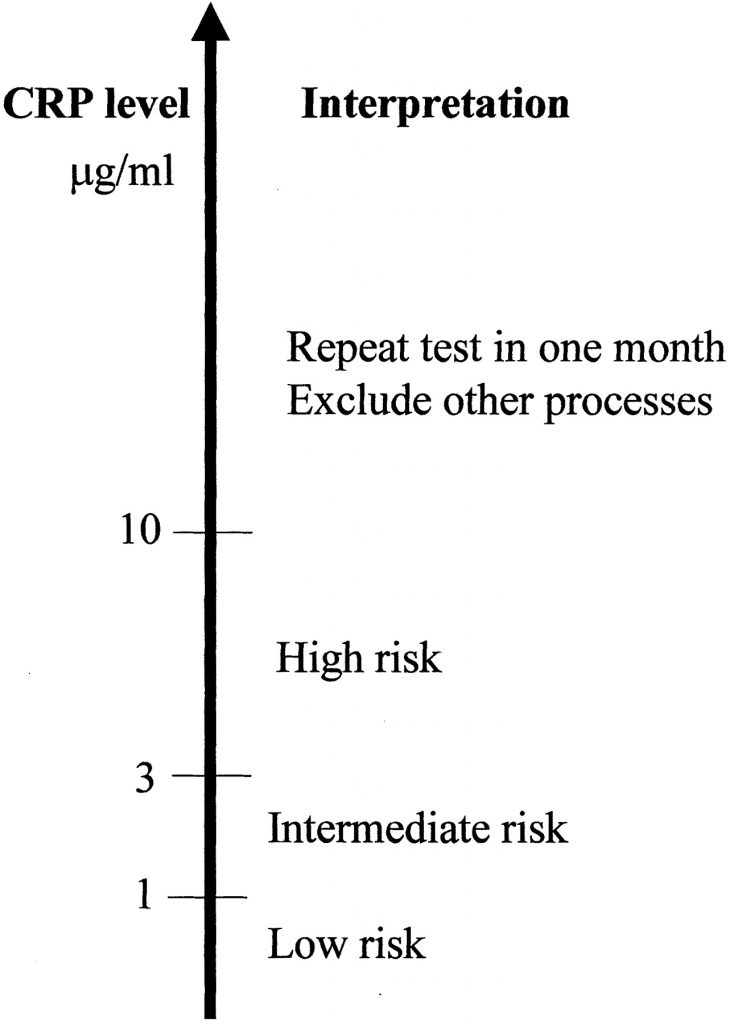
Look at the general guidelines for hs-CRP scores:
● Low risk of cardiovascular disease: Less than 1.0 mg/L
● Average risk: 1.0 to 3.0 mg/L
● High risk: Above 3.0 mg/L
A reading above 10 mg / L can signal the need for further testing to determine the cause of this significant inflammation in your body. Moreover, tests showing serum CRP levels above 10 mg / L in apparently healthy men or women should be repeated after a month3. This is done in order to exclude a latent infection or other systemic inflammatory process.
As you can see, a reading above 10 mg/L may signal a need for further testing to determine the cause of such significant inflammation in your body. It’s worth mentioning that levels of hs-CRP less than 10 mg/L are significant for cardiovascular risk stratification. Higher hs-CRP levels may be the sign of acute inflammation, a chronic illness, a trauma, etc.
C-Reactive Protein as a Biomarker of Cardiovascular Disease
In recent years, hs-CRP has been endorsed by several public health organizations as a biomarker of cardiovascular disease risk45.
As for primary prevention, a number of prospective epidemiological studies have shown that the high-sensitivity method in detecting CRP is highly predictive of cardiovascular accidents6, peripheral vascular diseases, ischaemic strokes, and sudden cardiac death risks even if the patient is virtually healthy. Other major studies in the USA and Europe have proven hs-CRP levels to be a better risk indicator than low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. Moreover, since hs-CRP reflects a different cardiovascular risk component, a combination of hs-CRP and lipoprotein profile would significantly enhance total risk estimation. Thus, LDLC levels higher than 160 mg/DL and high hs-CRP levels signal a need to discuss “aggressive” primary prevention and lifestyle changes with your doctor and start a drug therapy in case of therapeutic indications.
Do I need to check my hs-CRP levels if I feel well?
Factors that increase hs-CRP levels are quite numerous. They include obesity, elevated blood pressure, diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2, acute situational reaction, sleep disturbances, etc. In order to make allowance for all the major factors, Healsens will provide your physical assessment, generate your individual profile and help determine the necessity and frequency of controlling your hs-CRP levels.
Follow us on Facebook|| Instagram || Telegram || Youtube
What if my C reactive protein CRP level is high?
As we wrote above, for hs-CRP values exceeding 10 mg / L, it is recommended to undergo additional testing to find the causes of inflammation. Since such high levels of hs-CRP are associated with acute inflammation, chronic disease, trauma, etc.
For values below 10 mg / L, the good news is that giving up smoking, regular physical activity, as well as weight-reducing treatment, can lower basic hs-CRP level without any medical help. Healthy eating habits7, green tea89, controlled drinking, sufficient vitamin D1011, vitamin C12, and vitamin K13 in your body can also reduce the level of the reactive protein in the body.
In addition, glucosamine may reduce cancer mortality by lowering C-reactive protein levels. Therefore, if C-reactive protein is higher than 1 mg / L and there are no contraindications such as HOMA-IR14 is not increased, then therapy with this substance at a dosage of 1500 mg per day can reduce cancer mortality and overall mortality15. This is due to a decrease in inflammation, which will be reflected in a decrease in the inflammatory marker C-reactive protein, as expected by about 23%.
The same effect can be achieved through certain medications, such as16:
- cyclooxygenase inhibitors(Aspirin, Rofecoxib, Celecoxib)
- thrombocyte aggregation inhibitors (Clopidogrel, Abciximab)
- cholesterol management products (statins, ezetimibe, fenofibrate, nicotinic acid)
- beta-adrenergic blocking agents and angiotensin
- converting-enzyme inhibitors (Ramipril, Captopril, Fozinopril)
- anti-diabetes drugs (Rosiglitazone, Pioglitazone).
In case any medications must be taken, discuss your therapeutic regimen with your doctor.
» Discover everything about what your cholesterol results mean.
Ordering Blood Tests in the Netherlands
If you are interested in checking your hs-CRP level, you can easily purchase a blood test kit from Healsens.
1. Download the Healsens app from Google Play or the App Store, depending on your device.
2. Complete the registration process in the app.
3. Tap on the ”Order Blood Tests”.
4. Find the hs-CRP test and tap on the “Add to Cart” button. Proceed with the ordering process.
» Unlock Optimal Health: Discover How a Personalized Healsens General Check-up Plan Can Transform Your Well-being.
Note
If you want to assess your hs-CRP level but are not residing in the Netherlands or have opted for a different laboratory, Healsens cannot upload your blood test results for you. Nevertheless, you have the option to undergo the required tests at any laboratory in your country and manually input the obtained results into the application. Healsens will open more opportunities for you to naturally normalize your blood test results. Furthermore, you gain full access to investigate your health risk assessment based on the provided data.
FURTHER READING
Source: ©️2019 Healsens B.V. All right reserved
Follow us on Facebook|| Instagram || Telegram || Twitter || Youtube
Source: ©️2019 Healsens B.V. All right reserve
- Association of 10-Year C-Reactive Protein Trajectories With Markers of Healthy Aging: Findings From the English Longitudinal Study of Aging
- Interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein, successful aging, and mortality: the PolSenior study
- Coming of Age of C-Reactive Protein
- High-sensitivity C-reactive protein as a biomarker of risk in coronary artery disease
- 2019 Guidelines on Dyslipidaemias (Management of)
- High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein and Cardiovascular Disease Across Countries and Ethnicities
- Diet quality inversely associated with C-reactive protein levels in urban, low-income African American and White adults
- Green tea extract reduces blood pressure, inflammatory biomarkers, and oxidative stress and improves parameters associated with insulin resistance in obese, hypertensive patient
- Green Tea minimally affects Biomarkers of Inflammation in Obese Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome
- Interaction of Vitamin D and Smoking on Inflammatory Markers in the Urban Elderly
- Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on the Level of Circulating High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- A Meta-analysis of Randomized Control Trials: The Impact of Vitamin C Supplementation on Serum CRP and Serum hs-CRP Concentrations
- Relationship between vitamin K status, bone mineral density, and hs-CRP in young Korean women
- Oral glucosamine in doses used to treat osteoarthritis worsens insulin resistance
- Total mortality risk in relation to use of less-common dietary supplements
- C-reactive protein (CRP)-lowering agents

