Vitamin D Function As The Overall Health Hormone

Modern books on wellness management often mention Vitamin D. It is commonly called overall health hormone1. And it makes sense! Vitamin d function is to help prevent chronic diseases and affect people’s longevity in general. Meanwhile, vitamin D insufficiency affects almost 50% of the population worldwide. An estimated 1 billion people worldwide, across all ethnicities and age groups, have its deficiency. That is and why sustaining its optimum level is critically important for your health.
This article was last reviewed on 12 March 2020. This article was last modified on 10 February 2020.
What is unique about vitamin D is that we don’t only get with food but can also produce it in our body by being exposed to sunlight. It plays a major role in keeping bones healthy, therefore it insufficiency can lead to child rickets, and adult malacosteon (bone softening) and osteoporosis (bone loss). But this vitamin’s role is not limited to this function.
Role of Vitamin D
Some recent studies have shown that it sufficiency is also associated with lower risks of getting diabetes milletus, multilocular sclerosis, cardiovascular diseases2, and tuberculosis3.
RELATED ARTICLES
Besides, it is vital for a healthy immune system4. Without sufficient its amount our immune cells cannot properly react to threats, making our body more vulnerable to infections. In addition, vitamin D affects both inborn and acquired immunity.
It’s worth mentioning that vitamin D has anti-cancer effect for various types of cancer5. Emerging research supports the possible role of it against cancer, fractures and falls, autoimmune diseases6, influenza, type-2 diabetes, and depression. That’s why many health care providers have increased their recommendations for vitamin D supplementation to at least 1000 IU7. So, a meta-analysis published in 2007 showed that this supplementation was associated with significantly reduced mortality.
By now we have received the evidence of an increased risk of prostate and endometrium cancer, esophageal, stomach and pancreatic cancer, bladder and renal cancer, Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkins lymphoma caused by vitamin D deficit.
It is remarkable that randomized double-blind examination shows significant 60% decrease in general oncological risk among postmenopausal women who were treated with vitamin D and calcium, as opposed to those who received placebo treatment during 4 years of observation8. The studies show the optimum 25 (OH)D in blood serum for cancer prevention to be 40-60 ng/mL (100-150 nmoles/L).
In addition, lower levels of vitamin D adjusted for BMI are also associated with an increased risk of hypertension9. Therefore, given the relatively safe and inexpensive route of vitamin D supplementation, some studies recommend prescribing vitamin D to hypertensive patients who fall below the target.
Chronic fatigue, low spirits may also be caused by vitamin D insufficiency. Besides, muscle weakness is considered a clear indicator of its clinical deficiency. Clinical symptoms of myopathy deficiency include proximal muscle weakness, diffusive muscle pains, and balance disorder. It also reduces age-related and general inflammations, which is critically important for cognitive function retention.
Follow us on Facebook|| Instagram || Telegram || Youtube
How to Measure Vitamin D Levels
Your vitamin D can be tested in a blood test that measures its content (25-OH vitamin D). 25(OH)D is the main metabolite of vitamin D in the blood. The two main forms of 25(OH)D are cholecalciferol (D3) and ergocalciferol (D2). D3 is mainly formed in our skin under ultraviolet rays, while the source of D2 is food. Significantly, the concentration of 25(OH)D is made up of these two components, and both forms are measured equimolarly. 25(OH)D is considered the best indicator of vitamin D in the body. In the Healsens app, you can take 25-OH vitamin D tests to check your vitamin D levels. For this test, venous blood is taken, and you can get the results within a few days.
Sun Exposure and Vitamin D
As mentioned above, you can get enough vitamin D in daily sun exposure. It happens because sunlight enables our body to synthesize it from cholesterol. To achieve this effect, some scientists recommend exposing about a third of your skin to the sun. This means that for most fair-skinned people, wearing a T-shirt and shorts for 10-30 minutes three times a week during the summer will be sufficient10. People with darker skin may need a bit longer than this.
However, a Korean study did not confirm the effectiveness of this recommendation. The experiment was Korean adults aged 20–49 years with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels of < 20 ng/mL11.
The results showed that the sunlight exposure group showed a slight increase in serum 25(OH)D level. The sunlight exposure group had sunlight exposure on 20% to 30% of their body surface areas for 30–60 minutes per day, 3 times a week during the summer season.
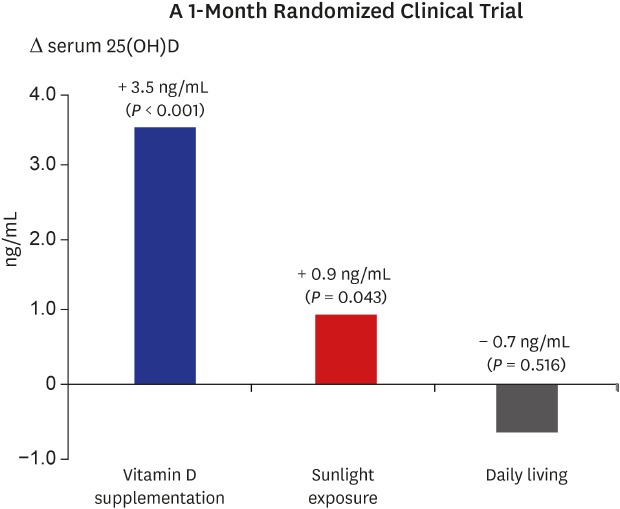
Let’s see how much of vitamin D can be obtained through sunbathing? A Norway study found that 30 minutes of midday summer sun exposure of the whole skin is equivalent to taking 10,000-20,000 IU vitamin D orally12. At the same time, the winter levels of vitamin D are 10 to 100% lower than the summer levels. That means people in Norway cannot get vitamin D from sunlight between October and March.
Several factors can influence your ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight. Firstly, it depends on the sensitivity of your skin to sunlight. Other contributing factors include the time of day, your skin color, and your proximity to the equator. Secondly, it’s important to consider the amount of skin exposed to sunlight and whether you’re wearing sunscreen.
Does sunscreen reduce vitamin D production?
Since we’ve mentioned sunscreen, let’s examine its impact on vitamin D levels. Some studies suggest that sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher can reduce vitamin D production by about 95–98%13. However, other studies have found that wearing sunscreen has only a minor effect on blood levels during the summer141516. The variations in results may be due to different factors and study durations. Another explanation could be that even when wearing sunscreen, prolonged sun exposure may still produce enough vitamin D. Therefore, the impact of sunscreen on circulating vitamin D levels remains a topic of debate.
In conclusion, to address the sunscreen dilemma, consider going without sunscreen for the first 10–30 minutes of sun exposure, depending on your skin sensitivity. Then, apply sunscreen before risking sunburn.
Precision Testing for Your Vitamin D Status
The most effective approach to evaluating your vitamin D levels is through blood analysis testing. Understanding these levels is crucial for various health reasons, and regular blood tests offer precise insights into your vitamin D status. Healsens not only provides a convenient option to order your blood analysis but also empowers you to interpret and respond to the results effectively. It’s important to note that a single test may not offer a complete understanding of your overall health. If your results reveal a deficiency, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized follow-up guidance. Maintaining a well-functioning immune system requires addressing lifestyle factors related to your vitamin D levels, and Healsens can assist you in crafting a customized Healsens Health Plan based on your results.
Ordering Blood Tests in the Netherlands
If you are interested in checking your HDL level, you can easily purchase a blood test kit from Healsens.
1. Download the Healsens App from Google Play or the App Store, depending on your device.
2. Complete the registration process in the app.
3. Tap on ”Order Blood Tests”.
4. Find the vitamin D and tap on the “Add to Cart” button. Proceed with the ordering process.
» Unlock Optimal Health: Discover How a Personalized Healsens General Check-up Plan Can Transform Your Well-being.
Note
If you want to assess your vitamin D level but are not residing in the Netherlands or have opted for a different laboratory, Healsens cannot upload your blood test results for you. Nevertheless, you have the option to undergo the required tests at any laboratory in your country and manually input the obtained results into the application. Healsens will open more opportunities for you to naturally normalize your blood test results. Furthermore, you gain full access to investigate your health risk assessment based on the provided data.
FURTHER READING
Follow us on Facebook|| Instagram || Telegram || Twitter || Youtube
Source: ©️2019 Healsens B.V. All right reserve
- Vitamin D and Chronic Diseases
- Vitamin D in Cardiovascular Disease
- Vitamin D deficiency and the risk of tuberculosis: a meta-analysis
- Vitamin D and the Immune System
- The Role of Vitamin D in Cancer Prevention
- Control of autoimmune diseases by the vitamin D endocrine system
- Vitamin D: The “sunshine” vitamin
- Vitamin D and Calcium Insufficiency-Related Chronic Diseases: an Emerging World-Wide Public Health Problem
- Vitamin D status and arterial hypertension: a systematic review
Recommended summer sunlight exposure levels can produce sufficient (> or =20 ng ml(-1)) but not the proposed optimal (> or =32 ng ml(-1)) 25(OH)D levels at UK latitudes- Can Current Recommendations on Sun Exposure Sufficiently Increase Serum Vitamin D Level?: One-Month Randomized Clinical Trial
- Sun and sun beds: inducers of vitamin D and skin cancer
- Sun and sun beds: inducers of vitamin D and skin cancer
- The effect of regular sunscreen use on vitamin D levels in an Australian population. Results of a randomized controlled trial
- Clinically prescribed sunscreen (sun protection factor 15) does not decrease serum vitamin D concentration sufficiently either to induce changes in parathyroid function or in metabolic markers
- Sunscreens block cutaneous vitamin D production with only a minimal effect on circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D

