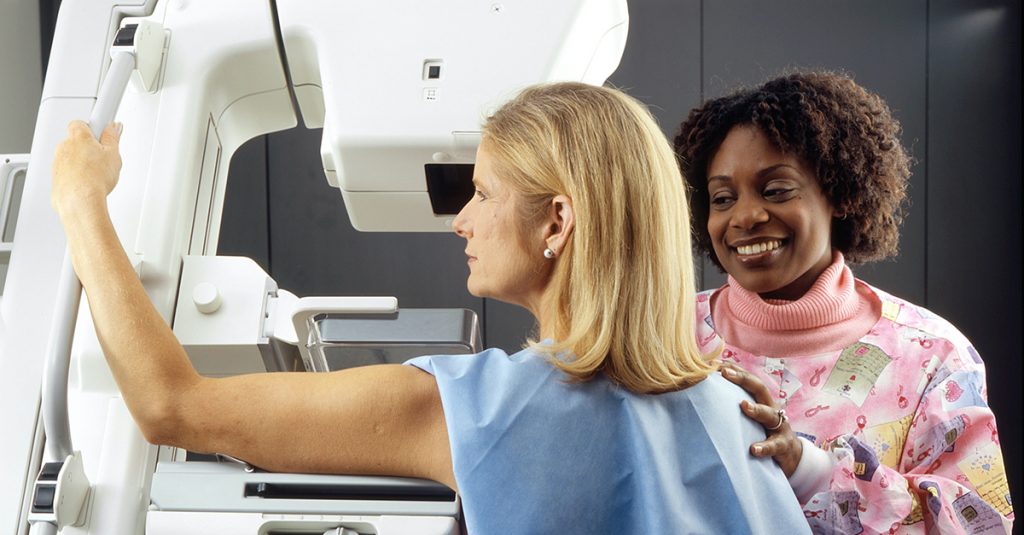
What Is A Screening Mammogram?
What Is A Screening Mammogram? Read More »
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | Records the default button state of the corresponding category & the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| pll_language | 1 year | The pll _language cookie is used by Polylang to remember the language selected by the user when returning to the website, and also to get the language information when not available in another way. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __utma | 2 years | This cookie is set by Google Analytics and is used to distinguish users and sessions. The cookie is created when the JavaScript library executes and there are no existing __utma cookies. The cookie is updated every time data is sent to Google Analytics. |
| __utmb | 30 minutes | Google Analytics sets this cookie, to determine new sessions/visits. __utmb cookie is created when the JavaScript library executes and there are no existing __utma cookies. It is updated every time data is sent to Google Analytics. |
| __utmc | session | The cookie is set by Google Analytics and is deleted when the user closes the browser. It is used to enable interoperability with urchin.js, which is an older version of Google Analytics and is used in conjunction with the __utmb cookie to determine new sessions/visits. |
| __utmt | 10 minutes | Google Analytics sets this cookie to inhibit request rate. |
| __utmz | 6 months | Google Analytics sets this cookie to store the traffic source or campaign by which the visitor reached the site. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CONSENT | 2 years | YouTube sets this cookie via embedded youtube-videos and registers anonymous statistical data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 5 months 27 days | A cookie set by YouTube to measure bandwidth that determines whether the user gets the new or old player interface. |
| YSC | session | YSC cookie is set by Youtube and is used to track the views of embedded videos on Youtube pages. |
| yt-remote-connected-devices | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt-remote-device-id | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
Choose either App Store or the Google Play, then scan the displayed QR code with your phone.